April 20, 2023
Environmental and Food Allergy Testing: A Comprehensive Guide for Patients and Families
Allergies can significantly impact a person’s quality of life, and accurate diagnosis is crucial for managing symptoms and avoiding potentially life-threatening reactions. Environmental skin testing and food allergy tests are effective tools healthcare providers use to diagnose allergies. This comprehensive guide to skin tests aims to provide patients and families with an understanding of the different forms of testing available and what to expect during the testing process.
Environmental Allergy Testing
Environmental allergy triggers, such as dust mites, pet dander, and pollen, can cause allergy symptoms. Environmental allergy testing can help patients identify the specific allergens causing their allergic symptoms and avoid them.
Food Allergy Testing
Food and specific food allergies can cause various symptoms, from mild itching and hives to life-threatening anaphylaxis. Food allergy testing can help patients identify the foods they are allergic to, allowing them to avoid and manage their food allergy symptoms well.
Several types of food allergy testing are available, including skin and blood tests. After completing the blood and/or skin test, an oral challenge may be considered to evaluate possible triggers further. The gold standard for diagnosing food allergies is the oral food challenge. Patients are given small amounts of a suspected food allergen under medical supervision to determine if they have a true food allergy.
Different Forms of Testing
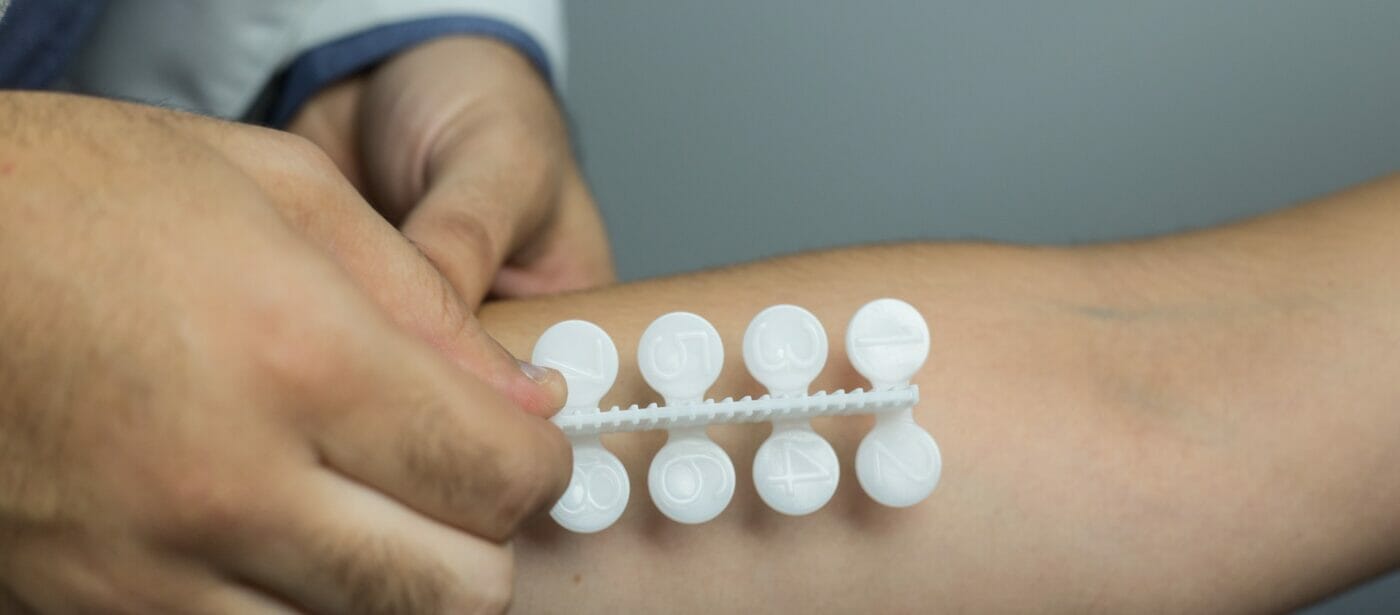
Skin Prick Test (SPT)
One of the most common allergy tests is the skin prick test. During this test, a healthcare provider will place a small amount of an allergen on the patient’s skin and prick the area to allow the allergen to enter the skin. The provider will then observe the area for a reaction, such as redness or swelling. This test can diagnose environmental and food allergies, and the skin prick test is generally quick and relatively painless.
It is essential to note that certain medications can interfere with SPT results, so patients should check with their healthcare providers to determine which medications should be avoided before testing. Patients should also be prepared to provide a detailed medical history to help guide the testing process.
Intradermal Test
Intradermal testing involves injecting a small amount of an allergen under the patient’s skin. It is used specifically for environmental allergy testing, is more sensitive than SPT, and may be used if the skin prick test results are inconclusive. While intradermal testing can produce more accurate results, it can also be uncomfortable and have a higher risk of false positives.
Preparing for Skin Testing
Before skin testing, patients should speak with their healthcare providers about any medications they are taking and how to prepare for allergy skin testing beforehand. Patients should also be ready to provide a detailed medical and food allergy diagnosis history to help guide the testing process.
It is recommended that patients wear loose-fitting clothing and avoid wearing any perfumes or scented lotions to the appointment. Patients should also bring a list of suspected allergens and relevant medical records.
During the Skin Testing Procedure
During the skin testing procedure, a healthcare provider will apply the allergen to the patient’s skin and observe the area for a reaction. The testing process can take up to an hour, and patients may be asked to remain in the doctor’s office for observation.
Interpreting Skin Test Results
A positive reaction to a skin test indicates that a patient has an allergic reaction to a particular allergen. However, it is essential to note that a positive test result on a scratch test does not necessarily mean a patient will experience allergy symptoms when exposed to the allergen.
False positives and negatives are possible in skin testing, so healthcare providers will use the test results combined with a patient’s medical history to diagnose. Additional testing may be required if the skin or blood test results are inconclusive.
After the Skin Testing Procedure
Following skin testing, patients may experience discomfort, such as itching, skin rash, or swelling at the test site. Over-the-counter antihistamines can help manage these symptoms.
Patients need to attend follow-up appointments and communicate any concerns or changes in symptoms with their healthcare providers. Based on the results of the skin testing, healthcare providers may recommend additional testing, such as blood tests or an oral food challenge, to confirm a diagnosis.
Allergy Diagnosis
Allergy diagnosis involves a combination of medical history, physical examination, and diagnostic tests, such as skin and blood tests. A healthcare provider will take an allergy test and use this information to make a diagnosis and develop a management plan tailored to the patient’s specific needs.
Medical History
A detailed medical history is crucial in diagnosing allergies. Patients should be prepared to provide information about their symptoms when they occur and any known triggers. Healthcare providers may also ask about family history, as allergies can be hereditary.
Physical Examination
A healthcare provider will look for signs of an allergic reaction during a physical examination, such as skin rashes or nasal congestion. The provider may also listen to the patient’s lungs and check for other physical symptoms.
Diagnostic Tests
Allergy testing, including skin and blood tests, can help healthcare providers diagnose allergies. Skin testing involves exposing the patient’s skin to small amounts of allergens to observe for a reaction. Blood testing involves taking a blood sample and measuring the levels of antibodies to specific allergens.
Treating Allergies
Once a diagnosis has been made, healthcare providers can work with patients to develop a management plan that includes avoiding known allergens and taking medications to manage symptoms. Patients with severe allergic reactions to certain foods may also be prescribed an epinephrine auto-injector to use in case of a life-threatening reaction.
Allergy Symptoms
Allergy symptoms can range from mild to severe and affect various body parts, including the skin, respiratory, and digestive systems. Common allergy symptoms include:
Environmental:
- Sneezing
- Itching of the nose, eyes or roof of the mouth
- Runny, stuffy nose
- Watery, red or swollen eyes (conjunctivitis)
Food-related:
- Abdominal pain/cramps
- Bloating
- Tingling/itching in the mouth
- Metallic taste in mouth
- Nausea and vomiting
- Difficulty breathing or shortness of breath
- Wheezing
- Swelling of the tongue
- Trouble swallowing
- Dizziness
- Weak pulse/drop in blood pressure
- Symptoms of shock such as skin rash (hives) and flushed skin
- Anaphylaxis which can be life threatening
Severe Allergic Reactions
Some patients may experience severe allergic reactions, especially to food, which can be life-threatening. Symptoms of a severe allergic reaction include:
- Difficulty breathing
- Swelling of the face, lips, tongue, or throat
- Rapid or weak pulse
- Loss of consciousness
Patients with a history of severe allergic reactions to certain foods should always carry an epinephrine auto-injector and seek medical attention immediately if they experience symptoms of anaphylaxis.
Conclusion
Accurate allergy testing is crucial for managing allergies and improving quality of life. Skin testing, including skin prick and intradermal tests, is a common and effective tool healthcare providers use to diagnose allergies. Patients should prepare for skin testing by providing detailed medical history and avoiding certain foods and medications before the appointment.
After testing, healthcare providers will use the results to make a diagnosis and develop a management plan tailored to the patient’s specific needs. Patients should attend follow-up appointments and communicate any changes in symptoms with their healthcare providers.
Accurate allergy testing is essential for managing allergies and avoiding potentially life-threatening reactions. If you suspect you have allergies, consult an allergy/immunology physician. He or she should be board-certified and have specialized allergy testing and treatment training. With proper diagnosis and treatment from allergy testing and an allergy/immunology physician, patients can manage their allergies and improve their quality of life.
